Scuba Diving Calculation Assistant App (Java) - 5/2022
A Java application designed to automate some simple and complex calculations that are common in the dive industry. The GUI was created from a text-based prototype using Apache NetBeans. Junit was used for unit testing.
Java JUnit Swing Apache NetBeans SVN IntelliJ Uni Project
Live Demo
Click here to try Scuba Diving Calculation Assistant on Replit
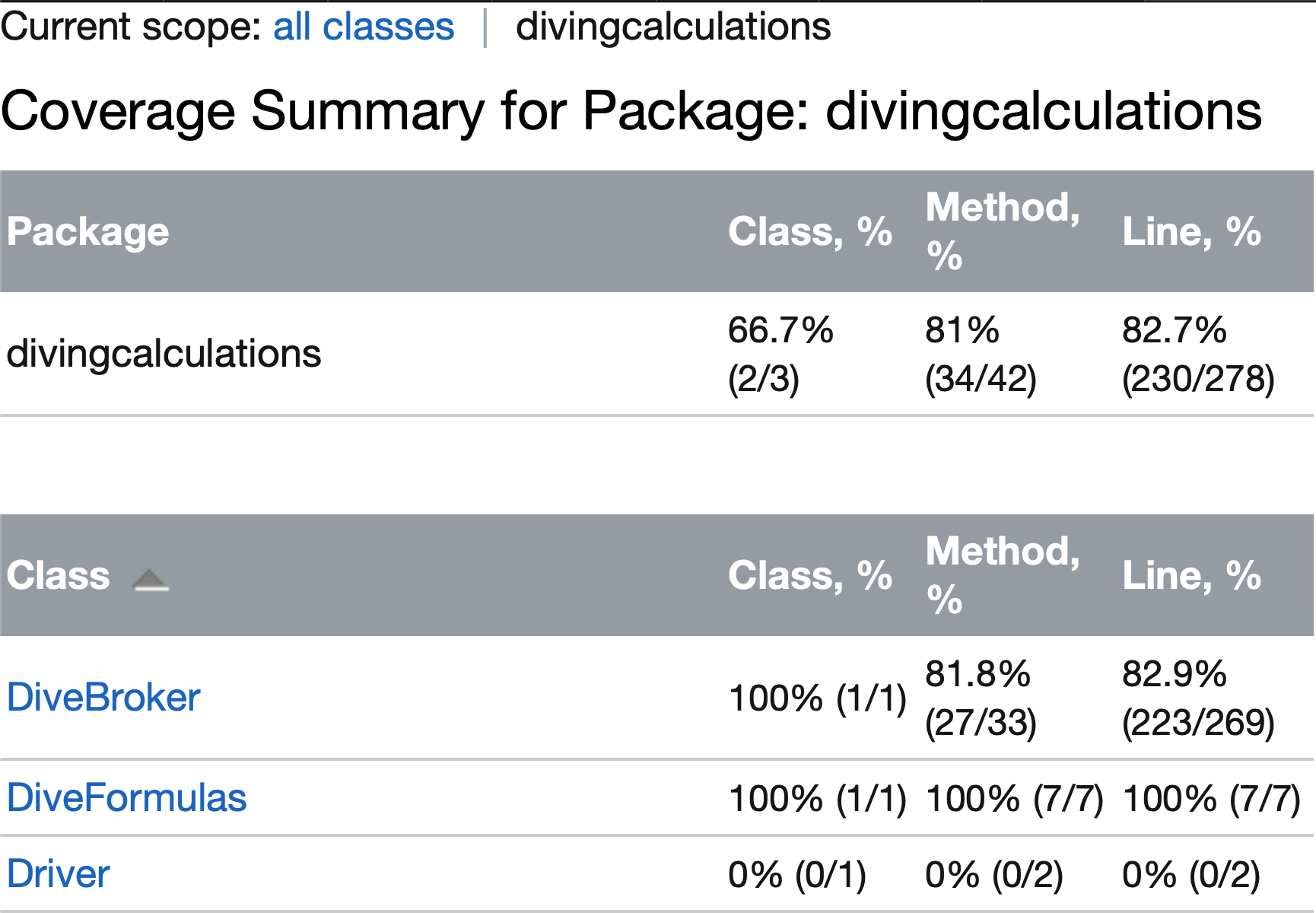
Screenshots
Overview
Purpose
Create an application in Java to automate some simple and complex calculations that are common in the dive industry.
Functionality
-
Simple Calculations:
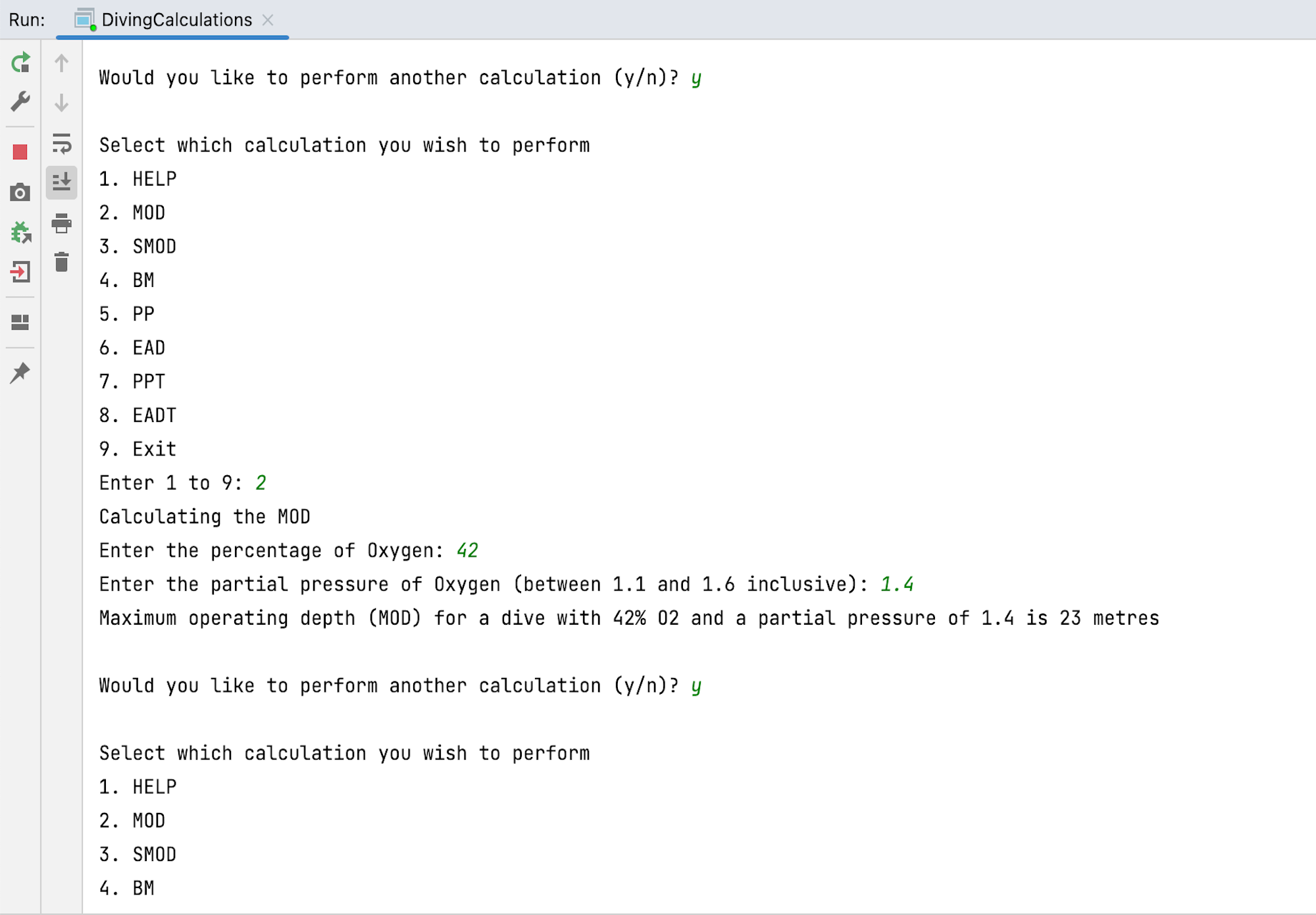
- Maximum Operating Depth (MOD)
- Standard Maximum Operating Depth (SMOD)
- Best Mix (BM)
- Partial Pressure of Oxygen (ppO2)
- Equivalent Air Depth (EAD)
-
Complex Calculations:
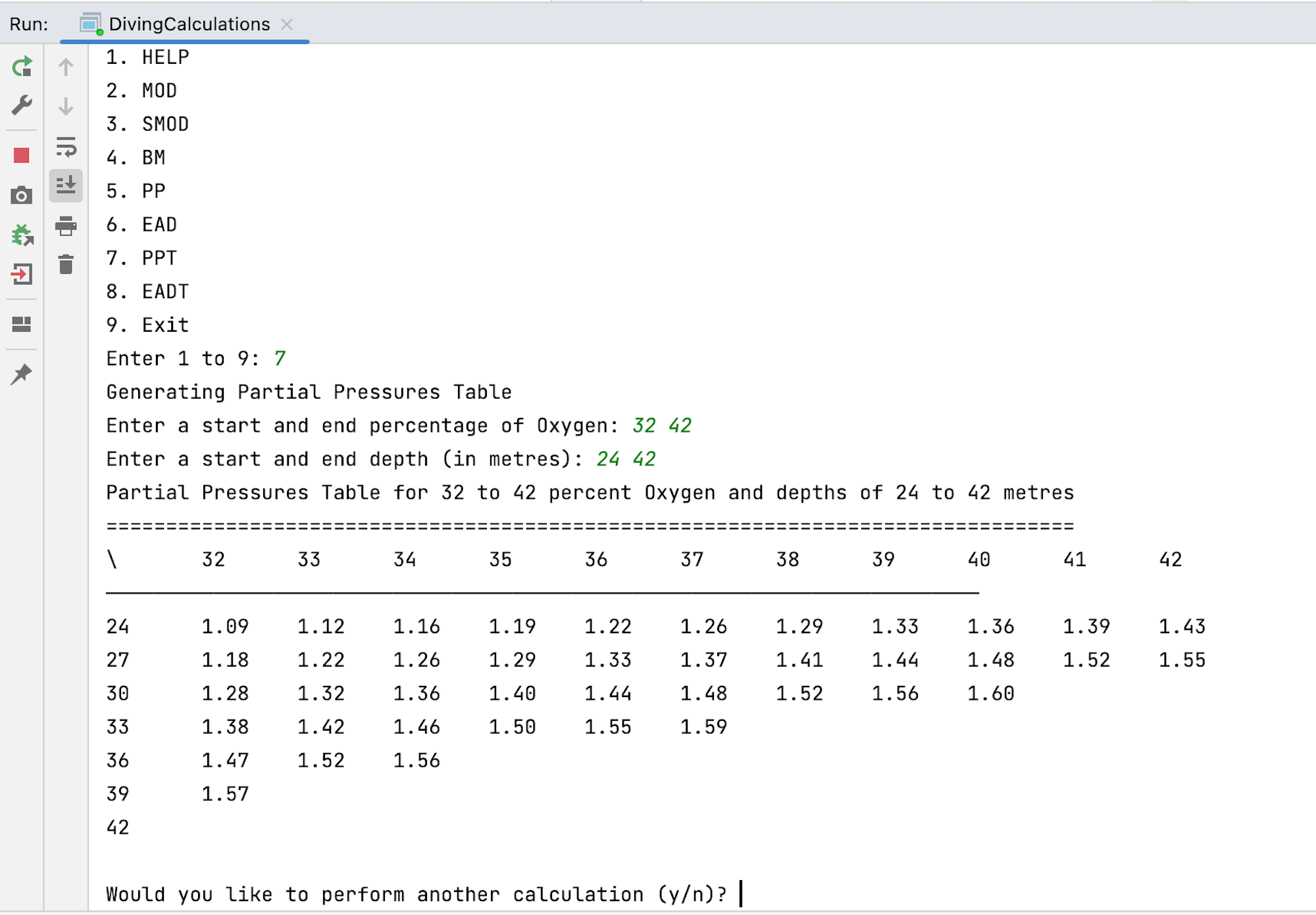
- Table of Partial Pressures (PPT)
- Equivalent Air Depth Table (EADT)
Target audience
- Divers
- Dive shop owners
Technical details
Technologies and Tools used
| Tech/Tool | Usage |
|---|---|
| Java | Programming |
| JUnit | Unit testing |
| SVN | Version control |
| Swing | GUI Framework |
| Apache NetBeans | GUI building |
| IntelliJ | IDE |
Tasks
- Build a text-based prototype that accepts user input and displays the requested calculation
- Use
JUnitfor unit testing - Build a functional graphical application
- Write appropriate
JavaDoccommenting and inline comments to assist future developers
Description
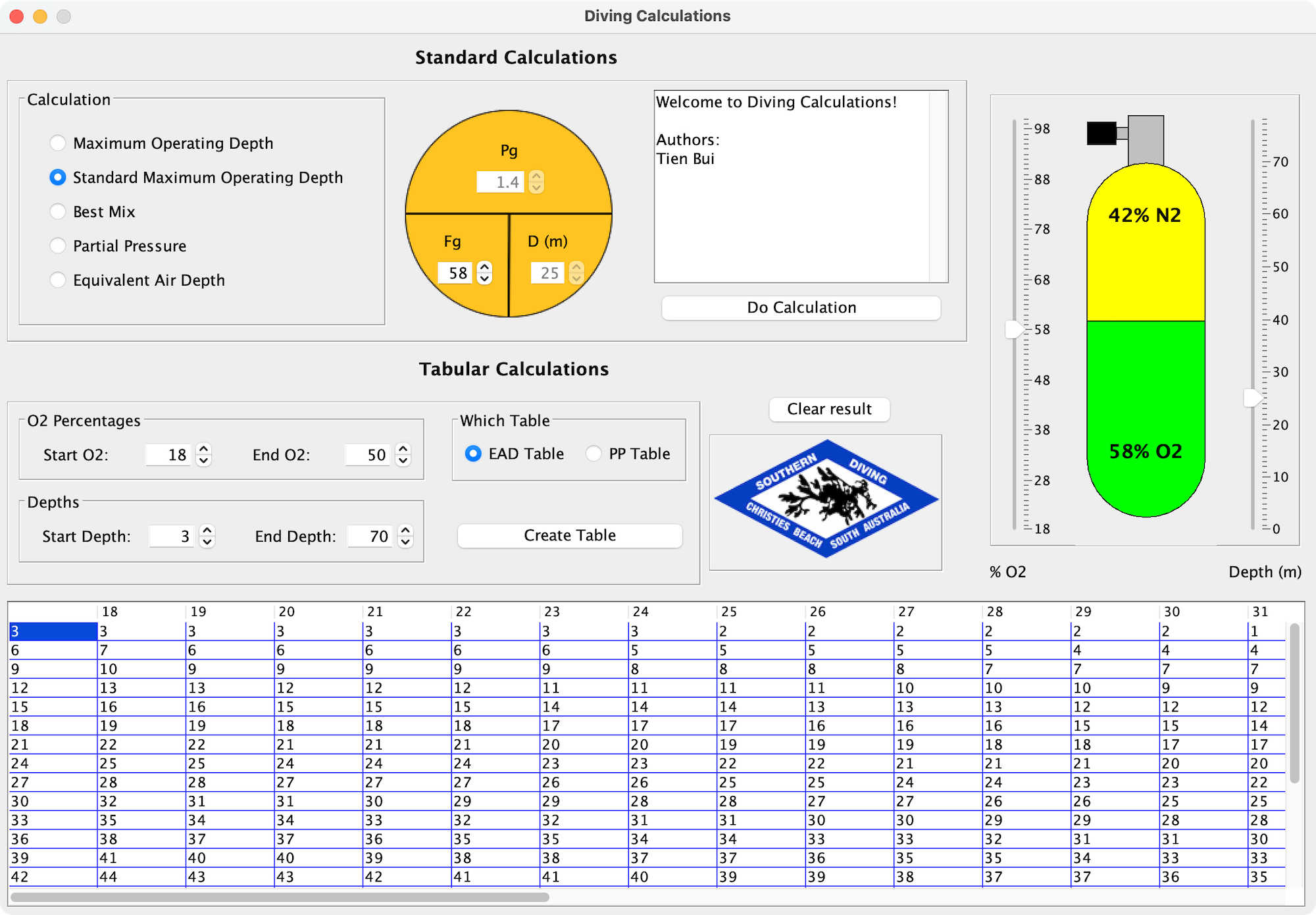
The Scuba Diving Calculation Assistant is a Java application designed to automate some simple and complex calculations that are common in the dive industry. It was created for a local dive shop owner who was tired of using a calculator to perform repetitive calculations. The application calculates the Partial Pressure of Oxygen (ppO2), Best Mix (BM), Maximum Operating Depth (MOD), and Equivalent Air Depth (EAD) for a requested input.
The underlying concepts and formulas used in scuba diving are provided in the application. Most of the time, divers breathe normal air, which comprises 21% Oxygen and 79% Nitrogen, which can be safely used to a depth of 68 metres. To avoid the risk of Central Nervous System (CNS) toxicity, the Partial Pressure of Oxygen (ppO2) in the mixture must be limited to a safe level of 1.1 ata to 1.6 ata inclusive.
The application uses a simple structure called the Circled T or T in the Circle to calculate the ppO2. In order to calculate the ppO2, we need to use another simple formula to convert depth in metres to ata. The application calculates the Maximum Operating Depth (MOD), Best Mix (BM), and Partial Pressure of Oxygen (PPO2) using these formulas. It also calculates the Equivalent Air Depth (EAD) to minimize Nitrogen Narcosis, which is calculated on mixtures of gas that contain more than the normal 21% of oxygen.
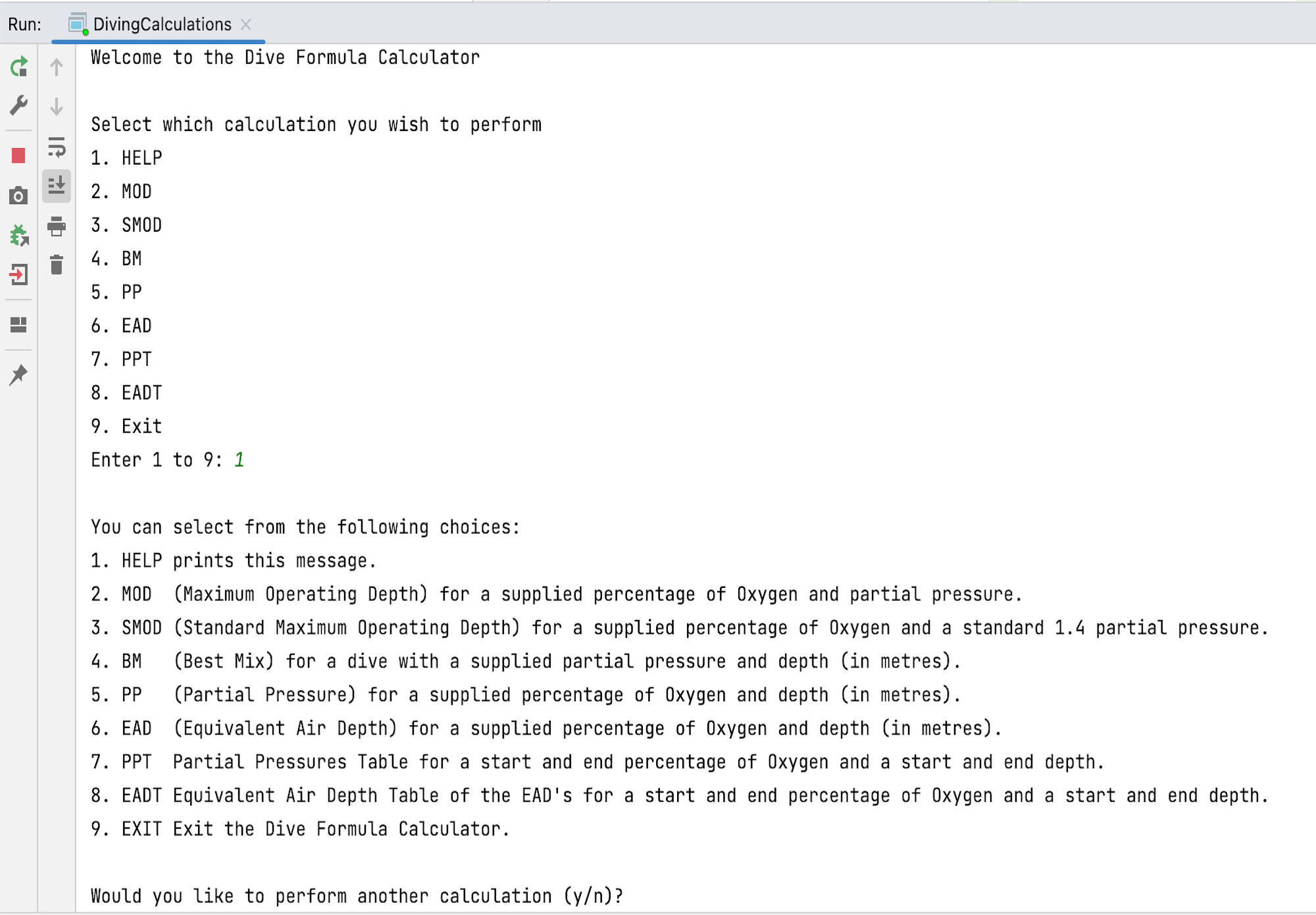
The prototype of the application is a text-based application that accepts user input and displays the requested calculation. The application ensures that all inputs are within the acceptable range and are suitable for the calculation selected. Errors are handled gracefully, and messages inform the user of the mistake and provide adequate opportunity to correct the error or perform another calculation.
In addition to the core algorithms, the application produces tables for Equivalent Air Depths and Partial Pressures. The application also calculates the SMOD, which is the most common partial pressure for the MOD calculation.
Overall, the Scuba Diving Calculation Assistant is an essential tool for divers to ensure that they stay safe while exploring the underwater world.
Source code
Unfortunately, this is a uni project and the source code cannot be shared due to academic integrity and intellectual property concerns.